Table of Contents
What Is a Mechanical Workshop?
A mechanical workshop is a space, often a garage or a large building, equipped with tools and machinery to repair or build mechanical items. The most common type is an auto workshop that focuses on vehicles, but some also work with farm equipment, industrial machinery, and bikes. Skilled mechanics work in these places to solve problems and perform maintenance.
Common Services Offered
Most mechanical workshops offer a wide array of services designed to maintain, repair, and enhance the performance of vehicles. Whether you’re driving a compact car, SUV, or light truck, these workshops provide essential services that help keep your vehicle safe, reliable, and running smoothly. Here’s a closer look at the most common services available:
1. Vehicle Servicing
Routine servicing is the backbone of vehicle maintenance. It typically includes oil and filter changes, fluid top-ups, brake inspections, and tire rotations. Regular servicing ensures that your vehicle performs efficiently, reduces the risk of breakdowns, and extends the engine’s lifespan.
2. Mechanical Repairs
Workshops are equipped to handle both minor and major mechanical repairs. These may involve replacing worn-out brake pads, fixing faulty clutches, repairing engines or transmissions, or addressing radiator leaks. Timely repairs prevent small issues from becoming costly problems.
3. Diagnostics
Today’s vehicles are loaded with electronic systems that often require specialized diagnostic tools to identify problems. If a warning light appears on your dashboard, mechanics can use computerized scanners to pinpoint issues in the engine, transmission, exhaust, or other systems.
4. Air Conditioning Service
In warm climates, a properly functioning AC system is essential. Workshops provide services like refrigerant recharging, checking for leaks, inspecting compressors, and replacing filters to keep your car cool and comfortable.
5. Suspension and Steering
These components are crucial for vehicle handling and safety. Mechanics check shocks, struts, steering racks, and linkages to ensure the ride is smooth and responsive. Any wear or damage is quickly addressed to prevent dangerous driving conditions.
6. Battery Replacement
If your car struggles to start or shows signs of electrical issues, the battery may be failing. Workshops offer battery testing and replacement services to ensure reliable performance in all weather conditions.
7. Wheel Alignment and Balancing
Poor alignment or unbalanced wheels can lead to uneven tire wear and a shaky ride. Regular alignment and balancing improve handling, fuel efficiency, and tire longevity.
8. Exhaust System Repairs
A functioning exhaust system reduces emissions, improves fuel economy, and prevents harmful fumes from entering the vehicle. Mechanics can replace damaged mufflers, pipes, or catalytic converters as needed.
These services ensure that vehicles remain in top condition, offering peace of mind to drivers and reducing long-term maintenance costs.
Tools and Equipment Used
A mechanical workshop is home to a wide variety of tools that help technicians and mechanics perform tasks efficiently. These tools range from basic hand tools to specialized instruments designed for precision, safety, and power. Understanding the types of tools found in a workshop can help anyone, from beginners to professionals, navigate their use and importance. Here’s a closer look at the different categories of tools commonly found in mechanical workshops.
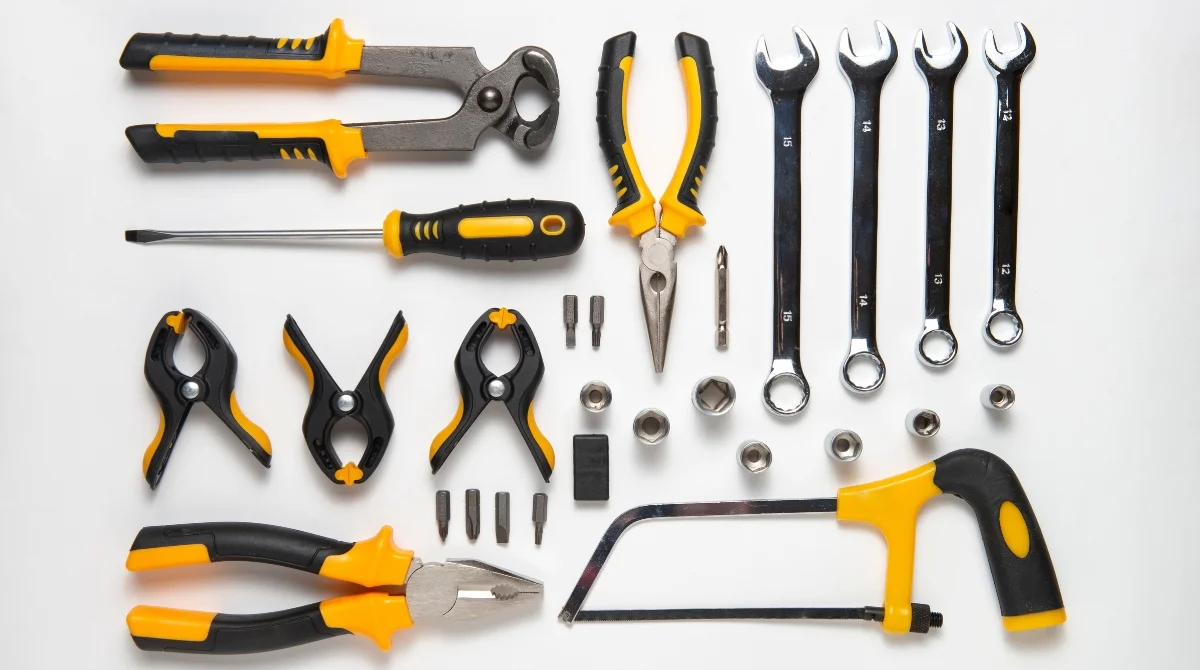

1. Hand Tools
Hand tools are the backbone of any mechanical workspace. They’re used in almost every task, from loosening bolts to adjusting delicate components.
- Wrenches and spanners: Used for gripping and turning nuts and bolts. They come in various types like open-end, box-end, and adjustable.
- Screwdrivers: These come in flathead and Phillips head types, essential for fastening and removing screws.
- Pliers: Including needle-nose, slip-joint, and locking pliers, used for holding, bending, or cutting wires and components.
- Hammers and mallets: Used for impact work like driving nails, aligning parts, or shaping metal.
2. Measuring and Marking Tools
Accuracy is crucial in mechanical work, and these tools ensure precise measurements.
- Tape measure: A flexible ruler used for general measurements.
- Vernier calipers: Help measure internal and external dimensions with high precision.
- Micrometers: Used for extremely accurate measurements of small items like shafts or bearings.
- Feeler gauges: Measure small gaps between parts, such as valve clearances in engines.
3. Power Tools
Power tools save time and reduce effort. They are driven by electricity or compressed air.
- Cordless drill: Used for drilling holes or driving screws quickly.
- Angle grinder: Cuts, grinds, and polishes metal surfaces.
- Impact wrench: Applies high torque to bolts, commonly used in automotive work.
- Air ratchet: Powered by compressed air to speed up repetitive tasks like bolt removal.
4. Specialty Tools
These tools serve specific functions and are designed for more technical jobs.
- Torque wrench: Ensures bolts are tightened to the correct specification.
- Pullers: Remove bearings or gears from shafts without damage.
- Brake caliper tools: Aid in the maintenance of brake systems.
- Oil filter wrench: Makes it easy to remove and install oil filters.
What Machinery can be found within a mechanical workshop?
In a mechanical workshop, you’ll find a wide range of machinery that helps with diagnostics, repairs, manufacturing, and maintenance tasks. These machines are essential for handling different types of mechanical jobs efficiently and safely. Here’s a breakdown of the common machinery you can expect to find.
1. Lifting and Hoisting Equipment
These are used to raise vehicles or heavy parts to allow access underneath or to move them around safely.
- Hydraulic car lifts (2-post, 4-post, scissor lifts): Used to raise vehicles for easier access underneath.
- Engine hoists (cranes): Help remove or install engines safely.
- Transmission jacks: Specifically designed for removing or installing transmissions.
- Trolley jacks and jack stands: For quickly lifting and supporting parts of a vehicle.
2. Diagnostic and Testing Machines
Used to check engine performance, detect faults, and identify issues in the vehicle’s electronic systems.
- OBD-II scanners (On-Board Diagnostics): Plug into a car’s computer to diagnose engine and system errors.
- Multimeters: Used to test electrical circuits, voltage, and resistance.
- Battery testers: Check the condition and charge of vehicle batteries.
- Smoke leak detectors: Used to find vacuum leaks in intake systems.
- Compression testers: Measure engine cylinder compression.
3. Repair and Service Machines
These machines help with actual repair work, component servicing, and part replacements.
- Tyre changers: Remove and install tires on rims.
- Wheel balancers: Ensure wheels are balanced to prevent shaking while driving.
- Brake lathes: Resurface brake rotors and drums for smooth operation.
- Air compressors: Power pneumatic tools like impact wrenches, spray guns, and inflators.
- Oil extractors and fluid pumps: Help change engine oil, transmission fluid, and coolant quickly.
- Welding machines: MIG, TIG, or arc welders for joining metal parts or fixing chassis damage.
4. Machining Equipment (For Fabrication and Custom Work)
These are typically found in workshops that also perform metalwork or part fabrication.
- Lathes: Shape, cut, or modify metal parts and rods.
- Drill presses: Drill accurate holes in metal components.
- Milling machines: Used for shaping or cutting metal with high precision.
- Grinders and bench grinders: Sharpen tools or clean rusted parts.
- Hydraulic presses: Press out bearings or shape metal parts.
5. Tool Storage and Organization Machines
Efficient work depends on having tools properly stored and accessible.
- Rolling tool cabinets: Store and organize hand and power tools.
- Workbenches with vises: Provide a stable surface for assembling or repairing parts.
- Parts washers: Clean grease and grime off engine parts and tools.
6. Ventilation and Safety Equipment
These are crucial for maintaining air quality and ensuring worker safety.
- Fume extractors: Remove exhaust fumes or welding gases.
- Fire extinguishers: Essential for handling oil, fuel, and electrical fires.
- First aid kits and eye wash stations: For handling emergencies.
- Proper lighting systems: Ensure visibility for precise work.
The Role of a Mechanic
A mechanic is a trained professional who works in a mechanical workshop. They know how different engines and machines work and how to fix them when something goes wrong. A good mechanic is skilled, detail-oriented, and patient. They often have to troubleshoot complex issues and explain the problem in simple terms to the customer. Being a mechanic also requires ongoing learning because technology in vehicles and machines keeps changing.
Benefits of a Well-Run Mechanical Workshop
A well-organized and professional workshop can offer many benefits not just to customers but to the community:
- Job creation: Mechanics, assistants, cleaners, and receptionists all find work in these places.
- Economic growth: By keeping transportation and machinery in good condition, workshops help other businesses run smoothly.
- Environmental care: Proper disposal of oil, batteries, and other waste helps protect the environment.
How to Choose the Right Workshop?
Choosing the right workshop for your vehicle or equipment servicing is essential for ensuring quality work and long-term reliability. With so many options available, here are some straightforward tips to help you make a confident decision:
1. Look for Experience and Reputation
A well-established workshop with years of experience is more likely to deliver dependable service. Ask friends, family, or colleagues for recommendations. Online reviews and ratings on platforms like Google or social media can also offer valuable insights into customer satisfaction.
2. Check for Certifications
Certified workshops often employ qualified technicians and use approved parts. Look for affiliations with recognized automotive organizations or manufacturer certifications. This indicates that the workshop meets industry standards.
3. Ask About Warranties
Reliable workshops stand by their work. Ask if they offer warranties on repairs and parts. This not only protects you financially but also reflects their confidence in the quality of service provided.
4. Visit the Workshop
A quick visit can reveal a lot. Clean, organized workspaces and courteous staff usually point to a professional and customer-focused operation.
5. Compare Prices
Get quotes from multiple workshops. While the lowest price isn’t always the best choice, comparing prices helps you understand the market and avoid being overcharged.
Future of Mechanical Workshops
As cars and machines become more advanced, workshops are also evolving. Electric vehicles (EVs), hybrid cars, and computer-controlled systems are now common. This means workshops need modern tools, and mechanics need updated training. In the future, we might see more eco-friendly workshops that focus on sustainability and use green energy. Digital records, online bookings, and mobile services are also becoming standard.
Conclusion
A mechanical workshop is more than just a place to fix broken cars. It’s a hub of technical skill, problem-solving, and customer care. From simple oil changes to complicated engine repairs, these workshops keep our lives moving by making sure the machines we rely on stay in top shape. Whether you’re a driver, a business owner, or just curious, knowing how a mechanical workshop works can help you take better care of your vehicles and appreciate the hard work that goes into keeping them on the road. Always remember, regular checkups and trusted mechanics go a long way in avoiding sudden breakdowns and costly fixes.









