Table of Contents
- A Brief History of CCTV
- How CCTV Systems Work?
- Types of CCTV Cameras: A Comprehensive Guide
- 1. Dome Cameras
- 2. Bullet Cameras
- 3. Pan-Tilt-Zoom (PTZ) Cameras
- 4. Infrared (IR) / Night Vision Cameras
- 5. Day/Night Cameras
- 6. Network / IP Cameras
- 7. Wireless Cameras
- 8. High-Definition (HD) Cameras
- 9. Thermal Cameras
- 10. Fisheye Cameras
- 11. Turret Cameras
- 12. Box Cameras
- 13. Hidden Cameras
- 14. Automatic Number Plate Recognition (ANPR) Cameras
- Applications of CCTV Systems
- Benefits of CCTV Systems
- Challenges and Concerns
- Global Perspectives on CCTV Usage
- Future of CCTV Systems
- Conclusion
Closed-Circuit Television, commonly known as CCTV, refers to a system where video cameras transmit signals to a specific set of monitors. Unlike broadcast television, the signal is not openly transmitted, ensuring that the footage remains within a closed system. CCTV systems are widely used for surveillance and security purposes across various sectors, including homes, businesses, and public spaces.
A Brief History of CCTV
The concept of CCTV dates back to 1927 when Russian physicist Leon Theremin developed an early mechanical CCTV system for the Soviet Union. This system was designed to monitor visitors approaching the Kremlin.
In 1942, during World War II, German engineer Walter Bruch designed a CCTV system to observe V-2 rocket launches. This system allowed for real-time monitoring but lacked recording capabilities.
The first commercial CCTV system, known as “Vericon,” became available in the United States in 1949, developed by Remington Rand. By the 1960s and 70s, CCTV systems began to be used in public spaces and businesses for security purposes.
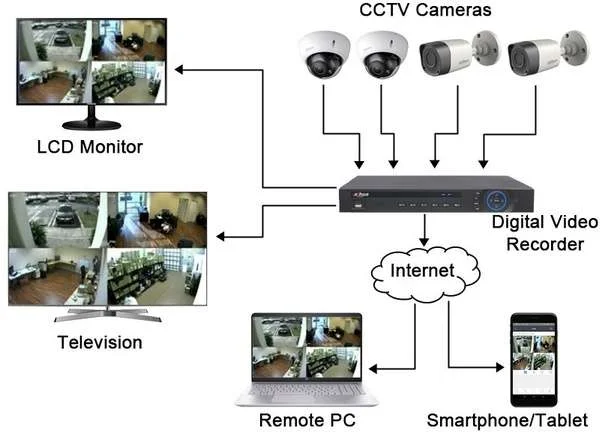
How CCTV Systems Work?
A basic CCTV system comprises several components working together to capture, transmit, and store video footage:
- Cameras: Capture video footage. They can be analog or digital (IP cameras).
- Lenses: Focus the captured images.
- Monitors: Display the live or recorded footage.
- Recording Devices: Store the footage for later review. This can be a Digital Video Recorder (DVR) for analog systems or a Network Video Recorder (NVR) for digital systems.
- Cables and Connectors: Transmit video signals from cameras to monitors and recording devices.
Modern CCTV systems may also include remote access capabilities, allowing users to view live footage via smartphones or computers.
Types of CCTV Cameras: A Comprehensive Guide
Closed-Circuit Television (CCTV) cameras are essential tools in modern security systems, offering various features tailored to specific surveillance needs. Understanding the different types of CCTV cameras can help you choose the right solution for your home, business, or public space.
1. Dome Cameras
Dome cameras are named for their dome-shaped housing, making them less obtrusive and suitable for indoor and outdoor use. Their design allows for a wider field of view and makes it difficult to determine the camera’s direction, deterring potential intruders.
Key Features:
- Vandal-resistant casing
- Infrared (IR) night vision
- Suitable for indoor and outdoor environments
Ideal For:
- Retail stores
- Restaurants
- Office buildings
2. Bullet Cameras
Bullet cameras have a long, cylindrical shape, resembling a bullet shell. They are typically mounted on walls or ceilings and are ideal for long-distance viewing. Their design makes them highly visible, which can act as a deterrent to criminal activity.
Key Features:
- Weatherproof housing for outdoor use
- High-resolution imaging
- Infrared night vision capabilities
Ideal For:
- Parking lots
- Building perimeters
- Industrial facilities
3. Pan-Tilt-Zoom (PTZ) Cameras
PTZ cameras offer the ability to pan (move horizontally), tilt (move vertically), and zoom in on specific areas. These features can be controlled remotely, allowing for real-time surveillance adjustments.
Key Features:
- Remote directional and zoom control
- High-resolution imaging
- Pre-set patrol patterns for automated surveillance
Ideal For:
- Large retail spaces
- Warehouses
- Public venues
4. Infrared (IR) / Night Vision Cameras
Infrared cameras are equipped with IR LEDs that allow them to capture video in complete darkness. They are essential for 24/7 surveillance in low-light or no-light conditions.
Key Features:
- Clear imaging in total darkness
- Automatic IR cut filters
- Suitable for indoor and outdoor use
Ideal For:
- Parking lots
- Alleyways
- Perimeter monitoring
5. Day/Night Cameras
Day/Night cameras are designed to function effectively in both well-lit and low-light conditions. They do not rely on infrared illumination, making them suitable for environments with varying lighting.
Key Features:
- Wide dynamic range (WDR)
- High-quality imaging in diverse lighting
- Weatherproof options available
Ideal For:
- Outdoor surveillance
- Building exteriors
- Parking areas
6. Network / IP Cameras
Network or IP cameras transmit video over the internet or local networks, allowing for remote viewing and storage. They offer high-resolution imaging and are often used in modern surveillance systems.
Key Features:
- Remote access via smartphones or computers
- High-definition video quality
- Scalable and flexible installation
Ideal For:
- Homes
- Offices
- Retail stores
7. Wireless Cameras
Wireless cameras transmit video signals without the need for cables, offering flexibility in installation. They are ideal for locations where wiring is challenging or for temporary setups.
Key Features:
- Easy installation
- Remote access capabilities
- Battery-powered options available
Ideal For:
- Rental properties
- Temporary surveillance needs
- Remote locations
8. High-Definition (HD) Cameras
HD cameras provide high-resolution video, allowing for clear and detailed images. They are essential in scenarios where identifying faces or license plates is crucial.
Key Features:
- 1080p, 4K, or higher resolutions
- Enhanced image clarity
- Zoom capabilities without loss of quality
Ideal For:
- Banks
- Casinos
- Retail environments
9. Thermal Cameras
Thermal cameras detect heat signatures rather than visible light, making them effective in complete darkness or challenging weather conditions. They are often used in high-security areas.
Key Features:
- Heat detection imaging
- Unaffected by lighting conditions
- Can see through smoke, fog, and dust
Ideal For:
- Critical infrastructure
- Border surveillance
- Industrial facilities
10. Fisheye Cameras
Fisheye cameras use ultra-wide-angle lenses to capture panoramic views, reducing the need for multiple cameras. They are suitable for monitoring large open areas.
Key Features:
- 180° or 360° field of view
- Minimal blind spots
- Compact design
Ideal For:
- Retail stores
- Warehouses
- Public spaces
11. Turret Cameras
Turret cameras, also known as eyeball cameras, have a ball-and-socket design, allowing for flexible positioning. They offer a balance between the features of dome and bullet cameras.
Key Features:
- Adjustable lens positioning
- Infrared night vision
- Discreet appearance
Ideal For:
- Residential properties
- Small businesses
- Indoor installations
12. Box Cameras
Box cameras are traditional CCTV cameras that offer high customization. They require separate lenses and housings, allowing for tailored surveillance solutions.
Key Features:
- Interchangeable lenses
- High-resolution imaging
- Customizable housing options
Ideal For:
- Banks
- Traffic monitoring
- Industrial settings
13. Hidden Cameras
Hidden cameras are designed to be inconspicuous, often disguised as everyday objects. They are used for covert surveillance.
Key Features:
- Disguised appearance
- Compact size
- Motion-activated recording
Ideal For:
- Nanny cams
- Theft detection
- Private investigations
14. Automatic Number Plate Recognition (ANPR) Cameras
ANPR cameras are specialized cameras designed to capture and read vehicle license plates. They are used in traffic management and access control systems.
Key Features:
- High-speed image capture
- Optical character recognition (OCR)
- Integration with databases
Ideal For:
- Parking lots
- Toll booths
- Secure
Applications of CCTV Systems
CCTV systems are employed across various sectors for multiple purposes:
1. Crime Prevention and Law Enforcement
CCTV acts as a deterrent to criminal activities. The presence of cameras can discourage potential offenders. Moreover, recorded footage can assist law enforcement agencies in investigating crimes and gathering evidence.
2. Traffic Monitoring
Traffic authorities use CCTV to monitor road conditions, manage traffic flow, and detect violations. This helps in reducing congestion and enhancing road safety.
3. Public Safety
In public spaces like parks, malls, and transportation hubs, CCTV systems help in monitoring activities, ensuring public safety, and managing large crowds during events.
4. Business Surveillance
Businesses use CCTV to monitor employee activities, prevent theft, and ensure the safety of both staff and customers. It also aids in resolving disputes by providing recorded evidence.
5. Home Security
Homeowners install CCTV systems to monitor their property, deter burglars, and keep an eye on deliveries or visitors. Modern systems allow remote access, enabling homeowners to view live footage from anywhere.
Benefits of CCTV Systems
Implementing CCTV systems offers several advantages:
- Deterrence of Criminal Activity: The presence of cameras can discourage potential criminals from engaging in unlawful activities.
- Evidence Collection: Recorded footage can serve as crucial evidence in legal proceedings or insurance claims.
- Remote Monitoring: Modern systems allow users to access live feeds remotely, providing peace of mind when away from the premises.
- Employee and Customer Safety: In workplaces and commercial establishments, CCTV ensures the safety of employees and customers by monitoring activities and identifying potential hazards.
- Cost-Effective Security: Compared to hiring multiple security personnel, CCTV systems offer a more affordable long-term security solution.
Challenges and Concerns
While CCTV systems offer numerous benefits, they also raise certain concerns:
1. Privacy Issues
The widespread use of surveillance cameras can lead to concerns about personal privacy. Individuals may feel uncomfortable being constantly monitored, especially in public spaces.
2. Data Security
CCTV systems, especially those connected to the internet, are vulnerable to hacking. Unauthorized access can lead to misuse of footage or breaches of sensitive information.
3. Maintenance Costs
Regular maintenance is essential to ensure the system functions correctly. This includes cleaning lenses, updating software, and replacing faulty components, which can incur additional costs.
4. False Sense of Security
Relying solely on CCTV for security can be misleading. Cameras can deter crime but may not prevent it entirely. It’s essential to integrate CCTV with other security measures.
5. Legal and Ethical Considerations
There are regulations governing where and how CCTV cameras can be installed. Unauthorized surveillance can lead to legal repercussions and ethical dilemmas.
Global Perspectives on CCTV Usage
The adoption and implementation of CCTV systems vary across countries:
1. United Kingdom
The UK is known for its extensive use of CCTV, especially in urban areas. While it has aided in crime prevention, debates continue regarding its impact on privacy.
2. China
China has one of the most extensive surveillance networks globally, employing advanced technologies like facial recognition. While it aids in maintaining public order, concerns about state surveillance and individual freedoms persist.
3. India
Major cities like Hyderabad and Delhi have seen a surge in CCTV installations to combat crime and enhance public safety. However, challenges remain in terms of infrastructure and maintenance.
Future of CCTV Systems
The evolution of technology continues to shape the future of CCTV:
1. Integration with Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI-powered CCTV systems can analyze footage in real-time, detect unusual activities, and send alerts, enhancing proactive security measures.
2. Cloud Storage
Storing footage in the cloud offers scalability, remote access, and reduces the risk of data loss due to hardware failures.
3. Enhanced Image Quality
Advancements in camera technology are leading to higher resolution footage, enabling better identification and analysis.
4. Wireless Systems
Wireless CCTV systems offer flexibility in installation and can be more cost-effective, especially in areas where laying cables is challenging.
Conclusion
Closed-Circuit Television systems have become an integral part of modern security infrastructure. From homes to businesses, traffic systems to public spaces, CCTV helps deter crime, enhance safety, and provide evidence when needed. As technology advances, these systems continue to evolve, becoming smarter, more accessible, and more efficient. However, as with any technology, responsible use is essential. Balancing security benefits with privacy concerns is key to ensuring CCTV serves the public good without infringing on individual rights.
Understanding CCTV doesn’t require technical expertise. It’s simply a system that watches and records, helping people stay safe and informed. Whether you’re a homeowner looking to protect your property or a business ensuring employee safety, CCTV offers a practical, effective solution worth considering.