Table of Contents
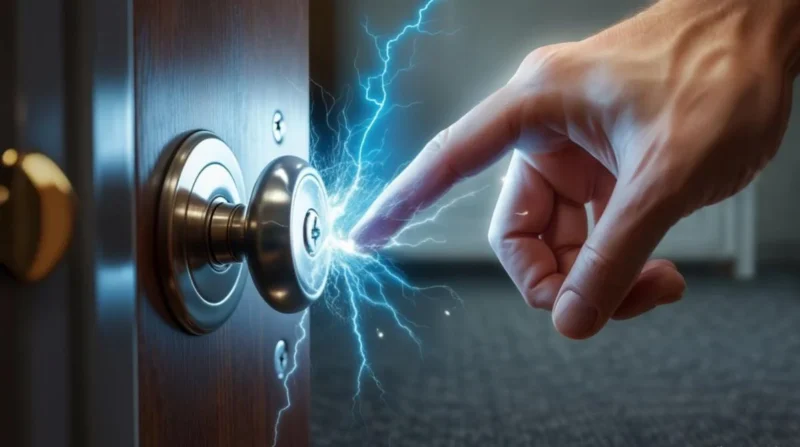
Electrostatic discharge, commonly known as ESD, is the sudden flow of electricity between two electrically charged objects. This phenomenon occurs when objects with different electrical charges come into contact or close proximity, leading to a rapid transfer of electrons. A familiar example is the small shock you might feel after walking on a carpet and touching a metal doorknob. While such instances are usually harmless to humans, ESD can pose significant risks to electronic devices. Even a discharge as low as 10 volts can damage sensitive components like hard drives or circuit boards.
How Does ESD Occur?
ESD typically results from the buildup of static electricity, which can happen through various means:
- Friction: Rubbing two different materials together can transfer electrons from one to the other, creating an imbalance of charges.
- Contact and Separation: Simply touching and then separating materials can lead to electron transfer.
- Induction: Bringing a charged object near a conductive material can cause a redistribution of charges without direct contact. When the accumulated static charge finds a path to discharge, such as touching a grounded object, ESD occurs.
Why Is ESD a Concern?
While ESD might seem trivial, its implications in various industries are profound:
- Electronics Manufacturing: ESD can damage or destroy sensitive components, leading to product failures.
- Medical Devices: ESD can compromise the functionality of critical medical equipment.
- Automotive Industry: Modern vehicles rely heavily on electronics, making them susceptible to ESD-related issues.
- Cleanroom Environments: ESD can attract contaminants, jeopardizing the integrity of products.
Moreover, ESD can cause latent defect damage that doesn’t immediately manifest but can lead to premature device failures.
Common Sources of ESD
Understanding where ESD can originate helps in its prevention:
- Human Body: Our bodies can accumulate static charges, especially in dry environments.
- Clothing: Synthetic fabrics can generate static electricity through movement.
- Work Surfaces: Desks and floors made of certain materials can contribute to static buildup.
- Packaging Materials: Plastic bags and foam can hold static charges that discharge upon contact with electronic components.
- Preventing ESD: To mitigate the risks associated with ESD, consider the following preventive strategies.
- Use Antistatic Wrist Straps: Wearing these straps grounds your body, preventing static buildup.
- Employ Antistatic Mats: Placing these mats on work surfaces and floors helps dissipate static charges.
- Control Humidity: Maintaining optimal humidity levels reduces static electricity generation.
- Wear Antistatic Clothing: Special garments minimize static charge accumulation on your body.
- Use ESD-Safe Packaging: Store and transport electronic components in antistatic bags or containers.
- Implement Grounding Techniques: Ensure all equipment and personnel are properly grounded to prevent charge buildup.
Why Is ESD Dangerous?
To people, ESD is often harmless. But for electronics, it’s a different story. Many modern devices use tiny components that can’t handle even small static shocks. ESD can cause:
- Instant damage: Parts inside devices like computers, phones, or TVs can stop working right away.
- Hidden damage: Sometimes the damage doesn’t show up immediately. A device might seem fine, but then break later.
- Data loss: In some cases, ESD can affect how devices store and transfer data.
Because of this, ESD is taken seriously in industries like electronics manufacturing, healthcare equipment, aerospace, and automobiles.
How to Prevent ESD?
The good news is that ESD is easy to control with some basic steps. Here are simple things anyone can do to avoid it:
- Use antistatic wrist straps: These are special bands that you wear on your wrist. They are connected to the ground to prevent your body from generating a charge.
- Antistatic mats: These mats go on tables or floors where electronics are handled. They help control the flow of static electricity.
- Keep air moist: Dry air makes static more likely. Using a humidifier helps reduce the chances of ESD.
- Wear proper clothing: Cotton is better than synthetic fabrics when handling electronics.
- Use antistatic packaging: Store electronics in special bags or boxes made to block static electricity.
- Touch grounded metal objects: Before handling devices, touch something grounded like a metal pipe or part of a grounded machine. This will help release any static from your body.
Who Needs to Worry About ESD?
While anyone can take precautions, these groups should be especially careful:
- Electronics repair workers: Even small charges can break the parts they’re fixing.
- People building computers: Computer parts like memory sticks or processors are easily damaged by ESD.
- Workers in electronics factories: High-volume production can lead to large losses if devices get damaged by ESD.
- Healthcare professionals: Devices used in hospitals and clinics need protection from static charges to ensure safety and accuracy.
- Automobile technicians: Modern cars use a lot of electronics, and ESD can damage sensors or controls.
International ESD Safety Standards
To reduce ESD risks, there are standards that companies follow. These standards guide how to set up workstations, train workers, and protect devices. Organizations around the world use these rules to make sure that sensitive components are safe from static damage. While regular users don’t need to know every detail, it shows how important ESD prevention is across industries.
- ANSI/ESD S20.20: Provides guidelines for developing an ESD control program.
- IEC 61340-5-1: Outlines general requirements for ESD protection in electronic devices.
Compliance with these standards helps organizations maintain product quality and reliability by minimizing ESD-related failures.
Conclusion
Electrostatic discharge may seem like a small thing, but it can have serious effects on today’s electronic devices. Understanding what causes ESD and how to prevent it can help protect your gadgets, save you money, and avoid headaches. Whether you’re working with electronics or just using them every day, being careful with static electricity is always a smart move.